
ABC Machinery Help Poultry Feed Mill Plant Setting Up
Investment And Regulatory Requirements For Starting A Poultry Feed Mill Plant
Establishing a modern poultry feed mill plant requires a structured investment plan that integrates financial, engineering, and regulatory considerations. Within the scope of poultry feed formulation, investors typically allocate between USD 350,000 and USD 5 million depending on capacity, automation level, and land costs. A facility designed for 10–20 TPH production often requires at least 3,500–6,000 m² of land, while higher-capacity systems above 30 TPH may exceed 8,000 m². Because a poultry feed mill plant must comply with feed safety regulations and environmental controls, approvals must be obtained before construction begins. The investment structure typically includes civil engineering costs, equipment procurement, installation fees, and utility infrastructure.
Capital Investment and Production Economics Framework
Building a modern feed pellet plant requires a clear understanding of how capital is allocated and how capacity decisions influence long-term profitability. Typically, 35–45% of total investment goes to core feed processing equipment (hammer mills, mixers, pelletizers), 25–30% to civil construction, and 10–15% to electrical and automation systems. Most feed mill projects also incur USD 20,000–50,000 in pre-operational expenses, including testing, commissioning, and trial runs.
Equipment cost scales sharply with plant capacity: a 1–5 TPH line generally requires USD 60,000–180,000, while high-throughput 20 TPH systems often exceed USD 850,000. These capital decisions directly shape production economics. For example, a 10 TPH plant running 22 hours per day at 85% efficiency can generate about 187 tonnes of feed daily. With industry margins of USD 12–18 per tonne, medium-scale plants commonly achieve net monthly profits of USD 50,000–90,000. At larger scales—especially above 30 TPH—unit energy consumption typically drops by 8–12%, further improving ROI and accelerating payback. (Related Post: Cost of Setting Up a Poultry Feed Mill>>)
Investment Cost Breakdown Table
| Investment Category | Typical Cost Share | Example Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Procurement | 35–45% | 250,000–850,000 |
| Civil Engineering | 25–30% | 150,000–600,000 |
| Electrical & Automation | 10–15% | 60,000–150,000 |
| Installation & Commissioning | 8–12% | 30,000–80,000 |
| Pre-Operational Expenses | 3–5% | 20,000–50,000 |
Other Key Investment Considerations
- Land Use Planning:Ensure at least 30–40% of land is reserved for raw material storage.
- Energy Cost Modeling:Pelleting consumes 8–12 kWh/ton, affecting multi-year profitability.
- Equipment Lifetime:Critical equipment such as pellet mills often have a 6–10 year service life.
- Dust Control Systems:Install cyclones and bag filters capable of handling 5,000–15,000 m³/h airflow.
- Working Capital:Maintain at least USD 80,000–120,000 for raw materials.

Profitable Feed Pellet Mill Plant Cost
Poultry Feed Mill Regulatory Licensing And Permits
An animal feed mill plant must obtain environmental impact assessment approval, a feed production license, and—when additives are included—specific additive-handling permits. Many jurisdictions require at least 2 rounds of facility inspection, including dust-control verification and raw material storage compliance. Key mandatory documents typically include:
- Feed production license
- Environmental approval certificate
- Fire and safety compliance confirmation
- Hazardous material handling registration when applicable
Unlock performance gains in your poultry feed mill investment — Connect with our engineering specialists to receive a customized cost and layout proposal.
Poultry Feed Mill Plant Layout And Production Line Design
Designing an efficient poultry feed mill plant layout begins with mapping material flow from receiving to finished pellets. A standard receiving section handles 20–60 tonnes of corn or soybean meal per hour, feeding into pre-cleaners and storage silos. Based on poultry feed formulation requirements, layout planning ensures the grinding, mixing, pelleting, cooling, and packaging sections are aligned along a single streamlined path. This minimizes crossflow and reduces truck loading time by 15–25%.
A well-configured production line includes a hammer mill sized between 55–110 kW, a mixer with 1,000–3,000 kg per batch capacity, and a pelletizer rated for 1–40 TPH output depending on plant scale. Automated batching systems are often calibrated for ±1% accuracy to support consistent nutritional composition. To meet broiler, layer, and breeder feed formula needs, design flexibility is crucial.
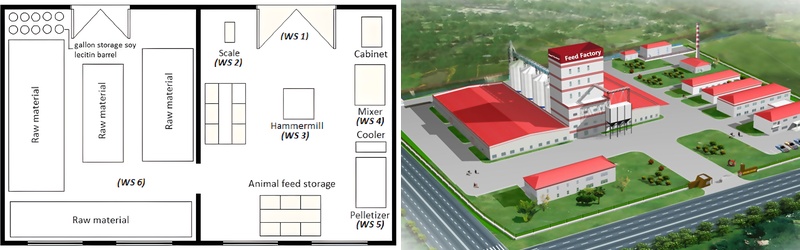
Poultry Feed Mill Plant Floor Workshop Design
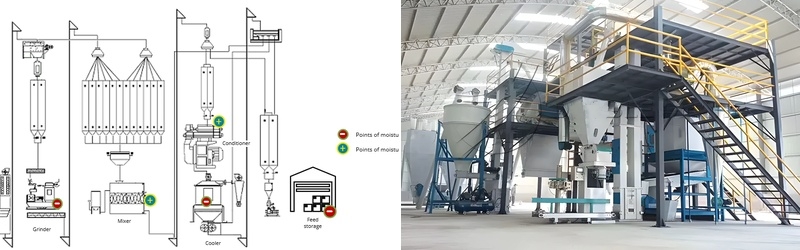
Chicken Feed Pellet Mill Plant Equipment Setup Design
Essential Equipment And Specifications Required In A Poultry Feed Mill Plant
A poultry feed mill plant requires several core machines, each contributing directly to feed quality. Hammer mills equipped with 3–5 mm screens deliver fine grinding needed for broiler diets, while double-shaft paddle mixers achieve CV ≤ 5% uniformity within 90–120 seconds. Pellet mills rated at 250–350 kW can produce up to 25 TPH, depending on die specifications.
Moisture control systems maintain pellet moisture within 11–13%, and coolers remove 70–90°C of heat from freshly pelleted feed. Automated bagging machines typically pack 10–50 kg bags at 6–12 bags per minute. As part of poultry feed formulation requirements, plants aiming for premium pelleted diets integrate screening systems with ≥95% pellet acceptance rate.
Optimize your equipment configuration with our project engineers to secure higher throughput and superior pellet durability.
Operating A Poultry Feed Mill Plant: Team Structure, Resources, and Profit Optimization Strategies
Operating a poultry feed mill plant requires a coordinated team of process engineers, quality control specialists, maintenance technicians, and formulation experts. A medium-scale mill producing 10–20 TPH typically needs 18–26 employees, including at least 3 skilled technicians for pelleting and automation systems. Production supervisors monitor real-time data extracted from MES (Manufacturing Execution System) platforms to track batch outputs, downtime, and material usage deviations of more than 2%.
Poultry Feed raw material sourcing contributes up to 70% of total production cost, making procurement efficiency essential. Corn and soybean meal prices fluctuate by 5–12% monthly, so diversified supplier contracts help stabilize poultry feed formulation costs. Plants adopting energy-efficient pellet mills can reduce power consumption by 8–10 kWh/ton, improving annual profitability by USD 30,000–60,000 for mid-size operations. Output stability above 90% significantly increases customer retention for layer and broiler integrators. (You May Interested in: Chicken Broiler Layer Feed Formulations>>)
Implementing preventive maintenance schedules every 500–800 hours of machine runtime reduces unplanned downtime by 20–30% annually and ensures consistent pellet quality for breeder and broiler customers.
Strengthen your feed plant’s profitability — Contact us to design a customized operational strategy aligned with your production goals.

 Build Your Future!
Build Your Future!











